1. Basic authoring, solving and reviewing
| Organize and navigate ↓ and → |
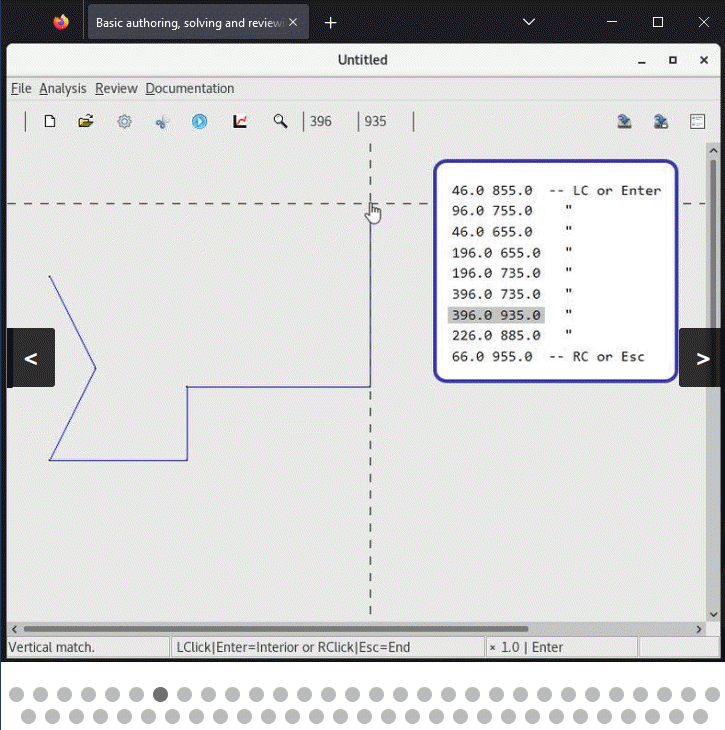
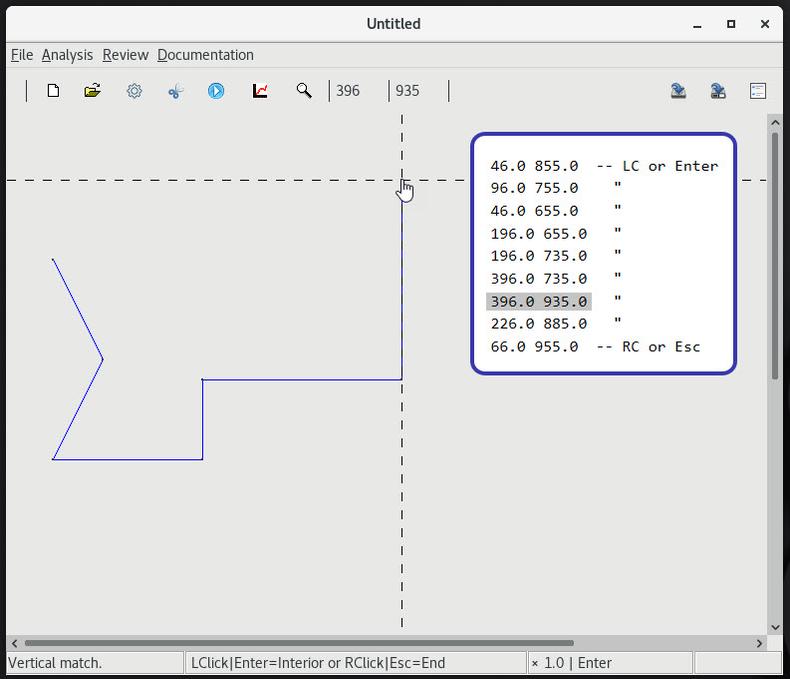
1 Make a polygonal base layer |
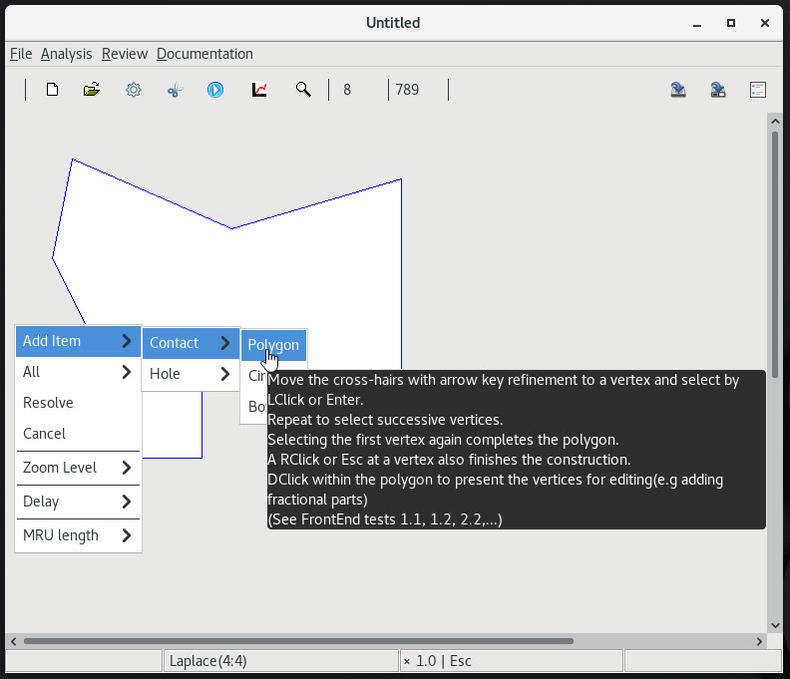
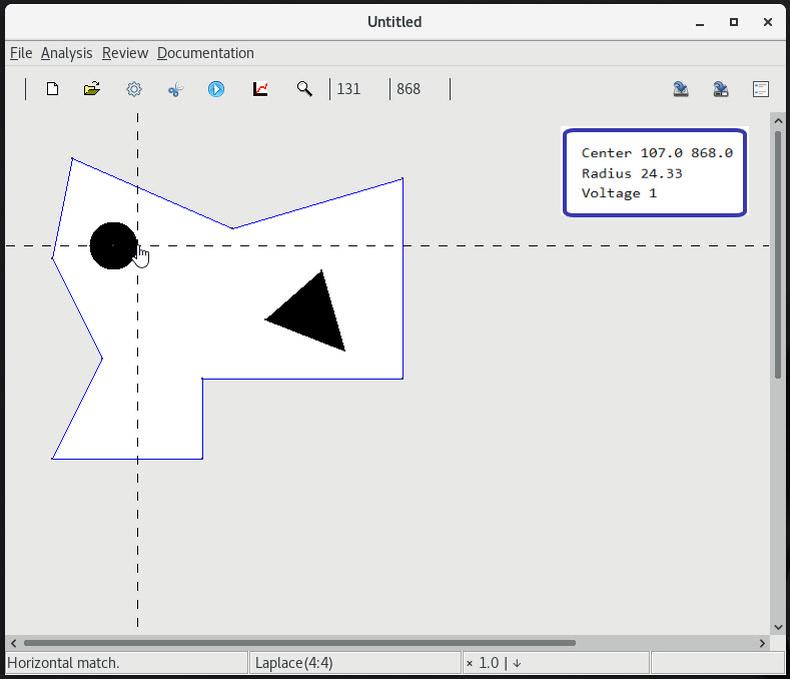
2 Add a triangular contact at the default voltage zero |
3 Add a circular contact at voltage one |
4 Basic solving |
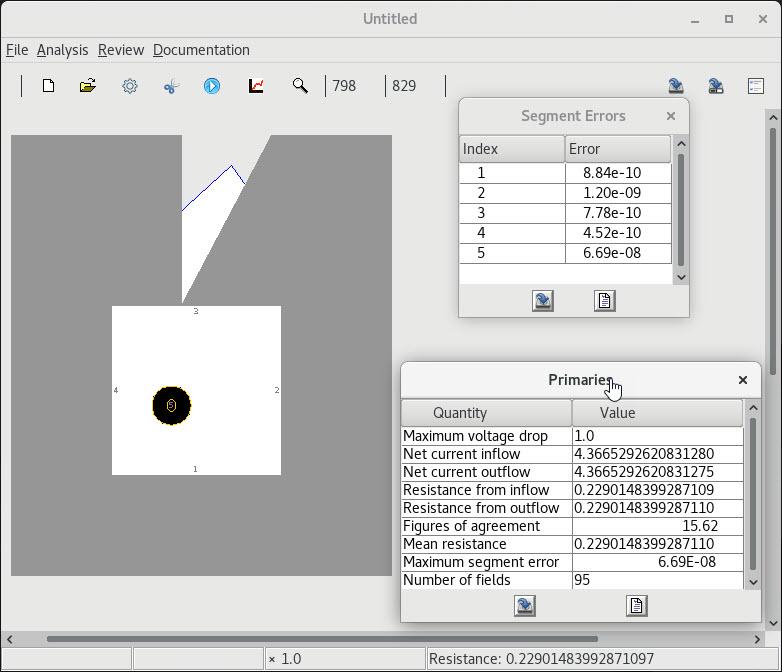
5 Fields and errors on an internal polygon |
6 Fields and errors on an outer boundary |
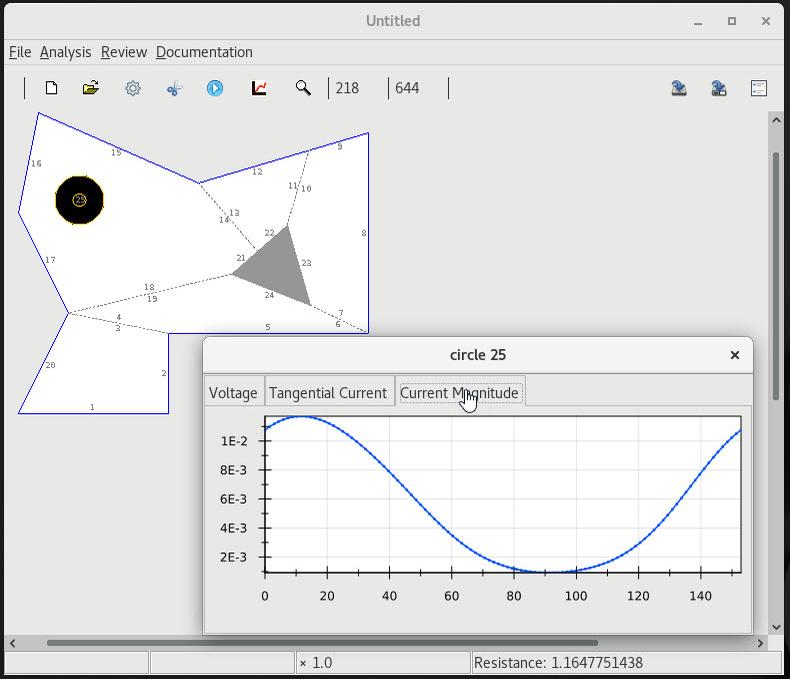
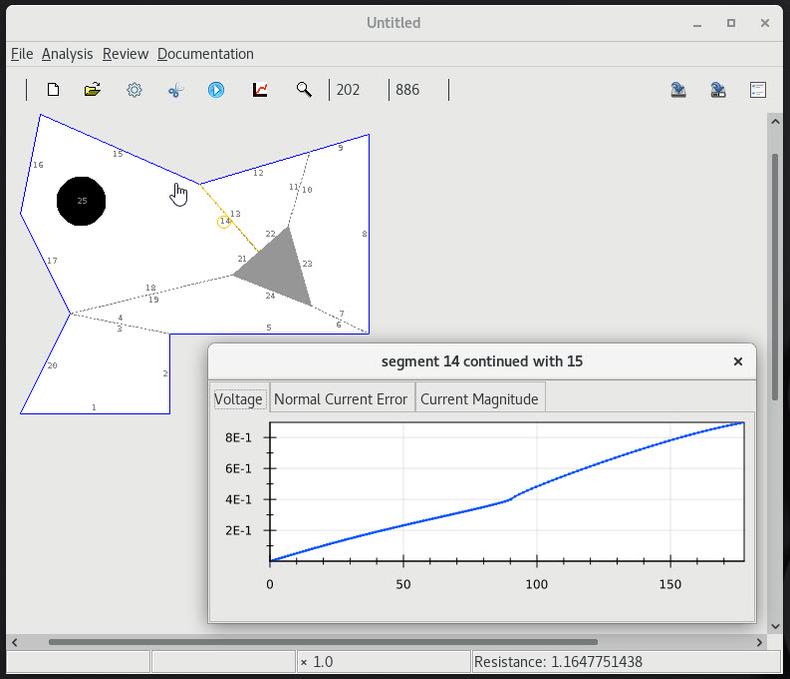
7 Fields and errors on a circular contact |
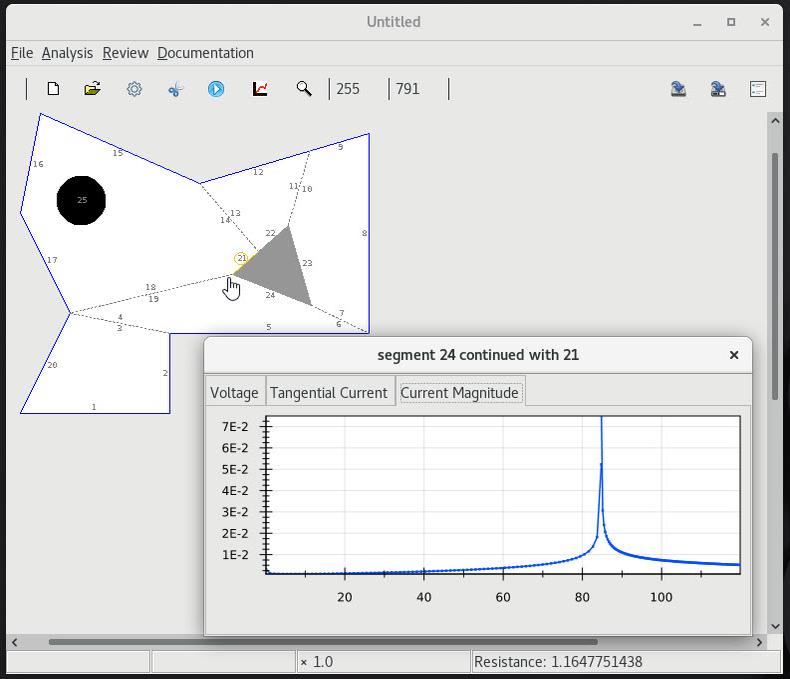
8 Fields and errors on a continuity cut |
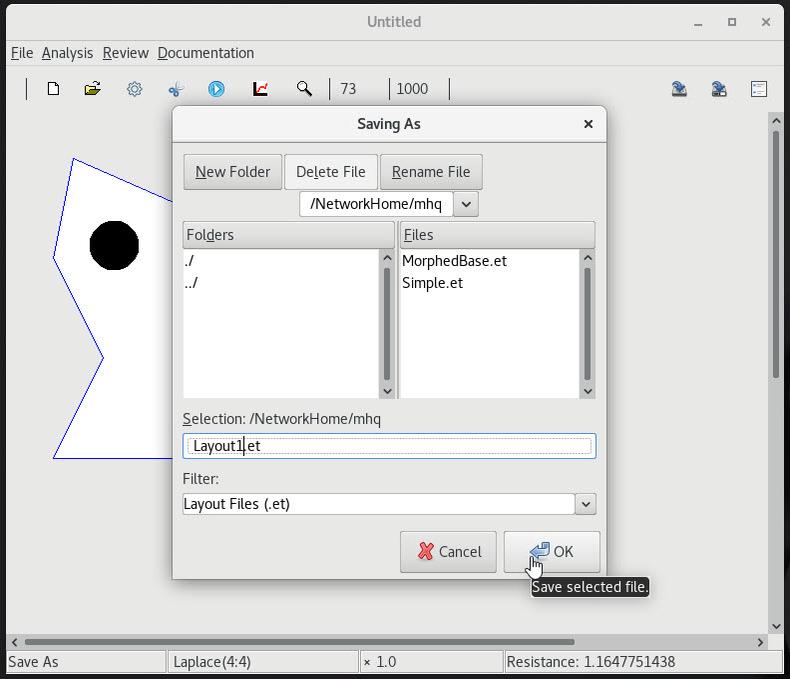
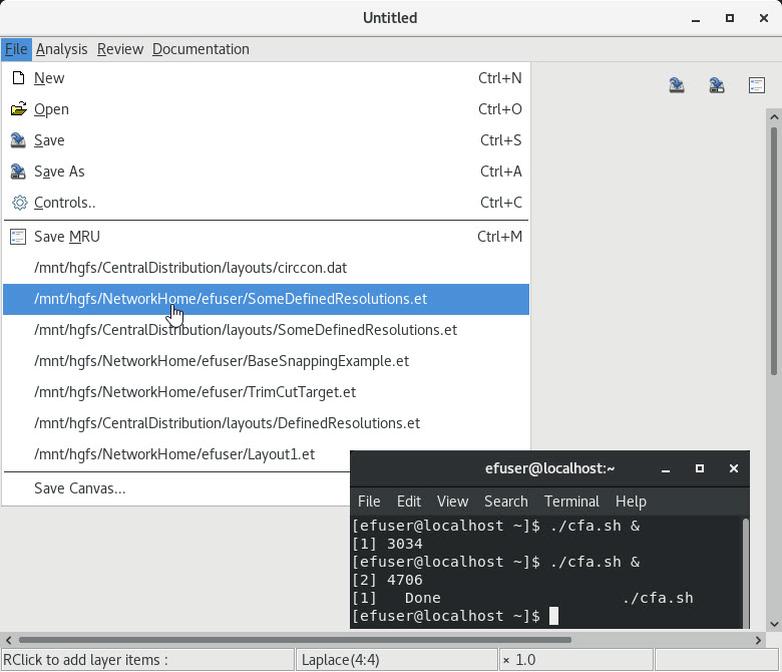
9 Saving the layout and state |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2. State restoration and float additions
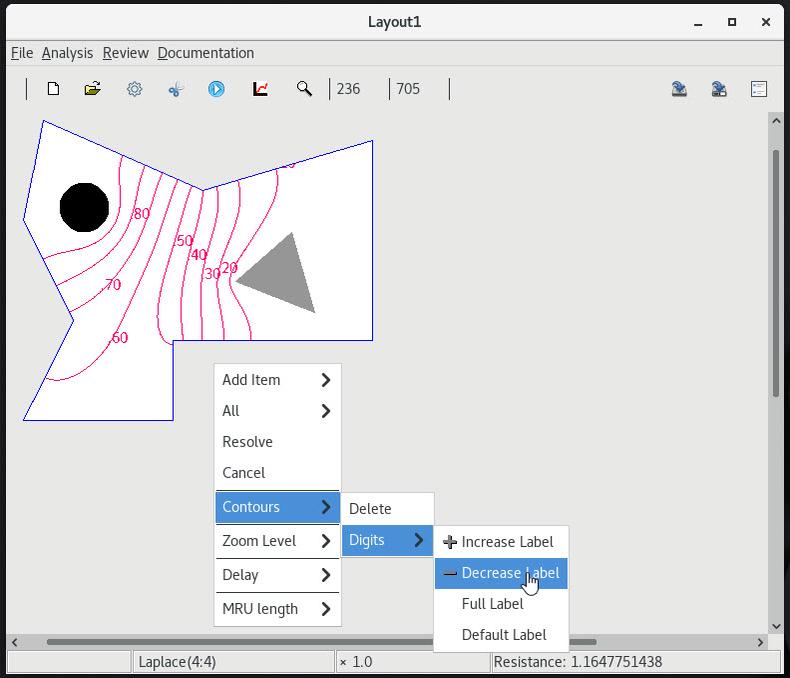
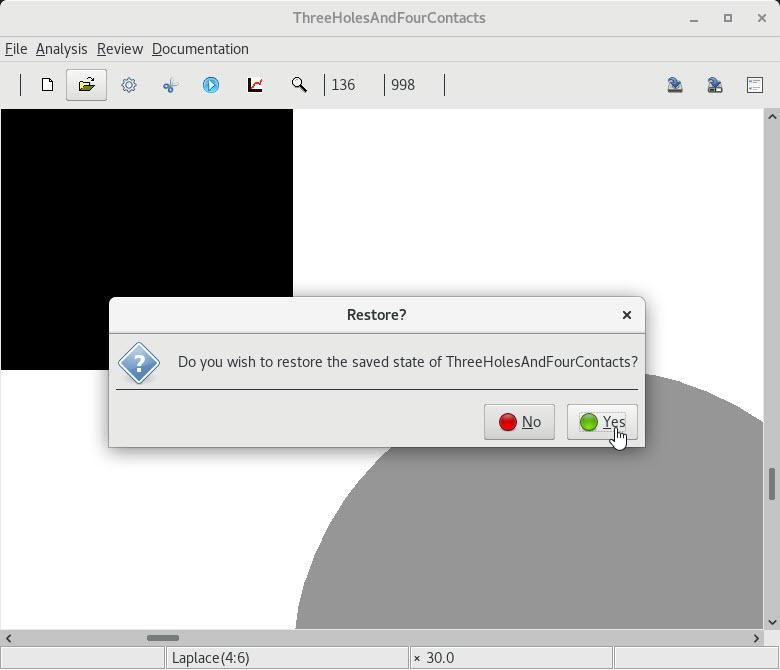
| 1 Restoring a solved layout and computing voltage contours |
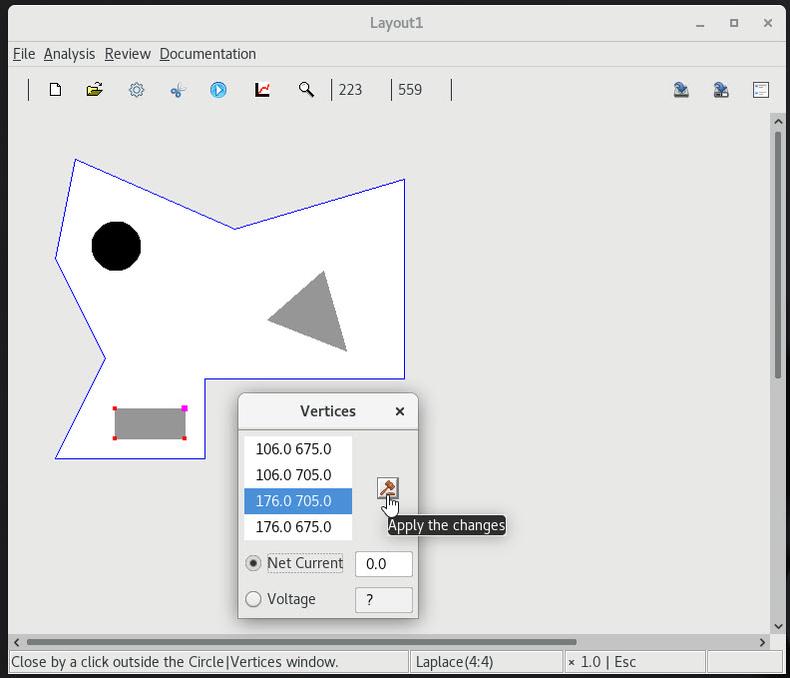
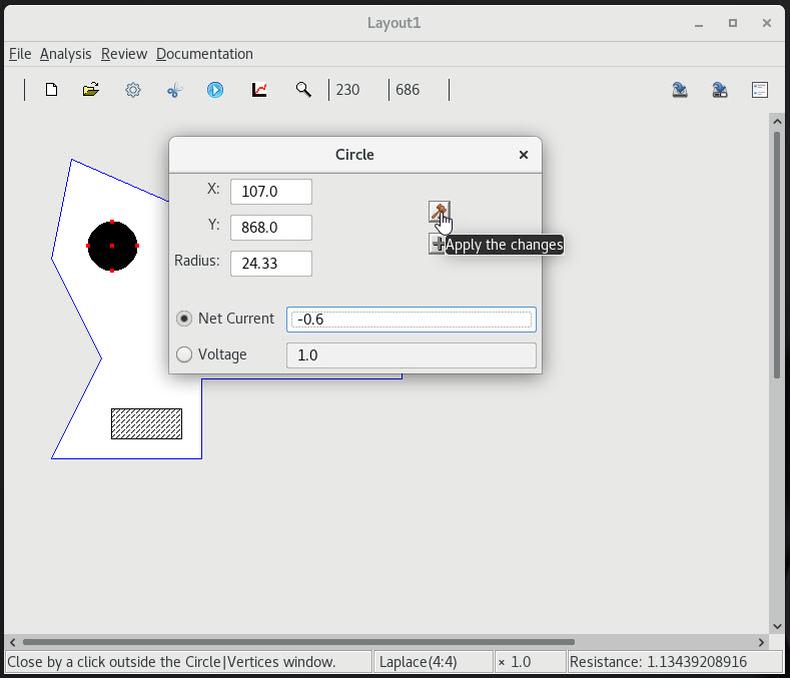
2 Adding a rectangular contact and setting float conditions |
3 Converting a circular contact to a float |
 |
 |
 |
3. Contouring
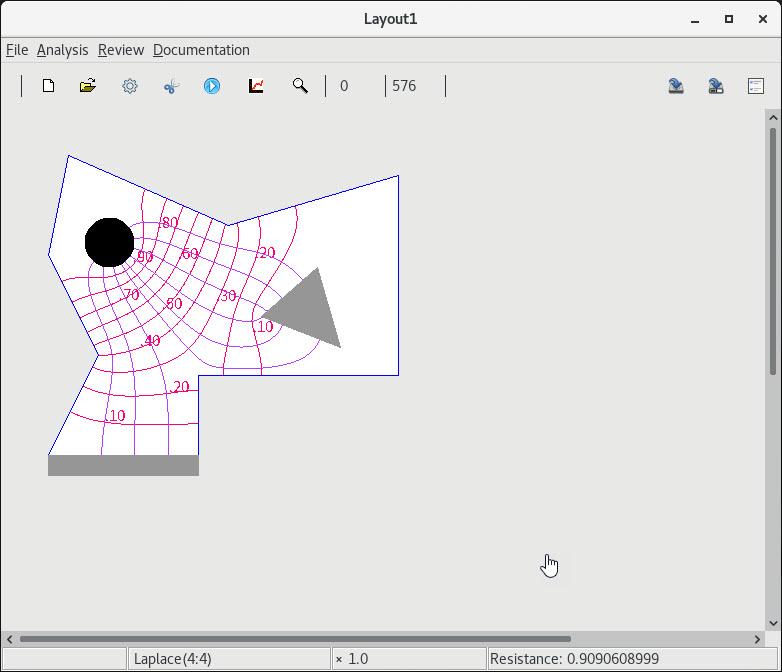
| 1 Bar contact and voltage-flowLine grid |
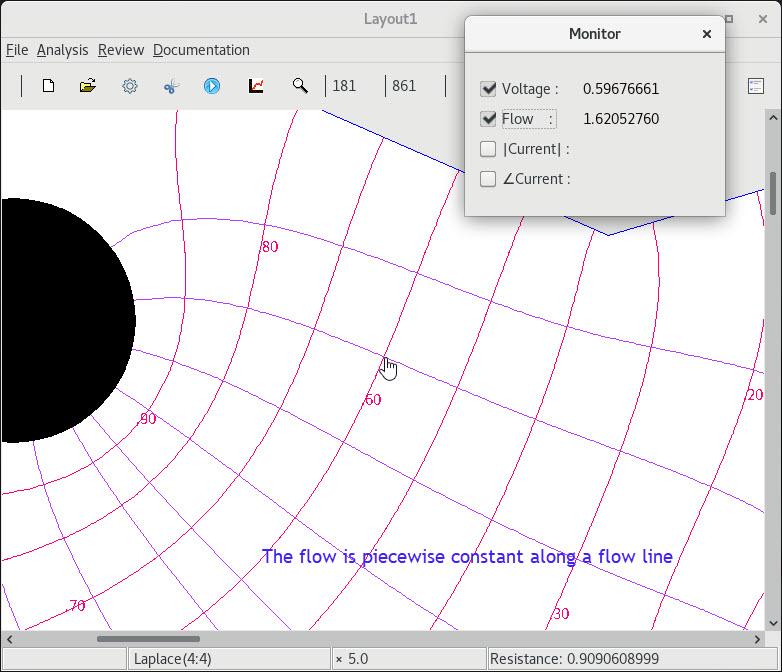
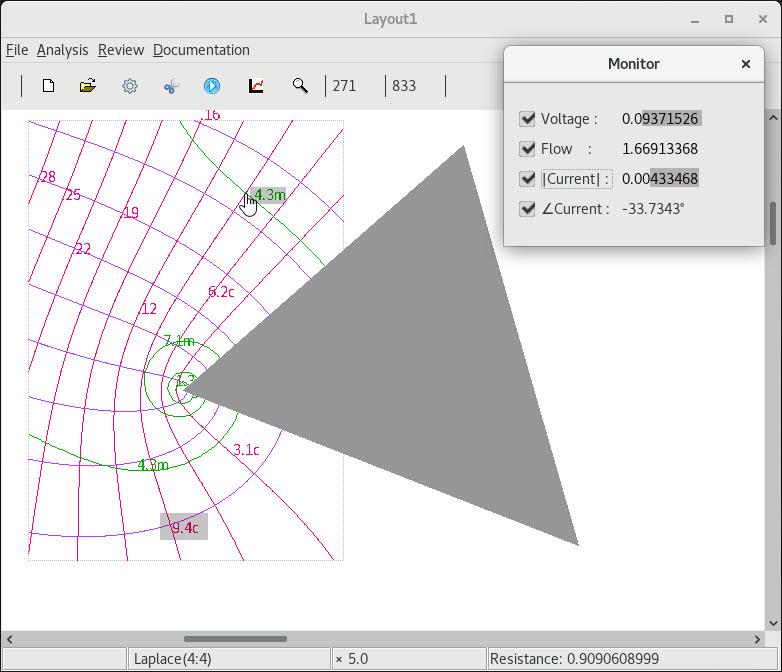
2 Multi-valued flow lines |
3 Retaining previous settings |
 |
 |
 |
4. Working with layouts given in the dat format
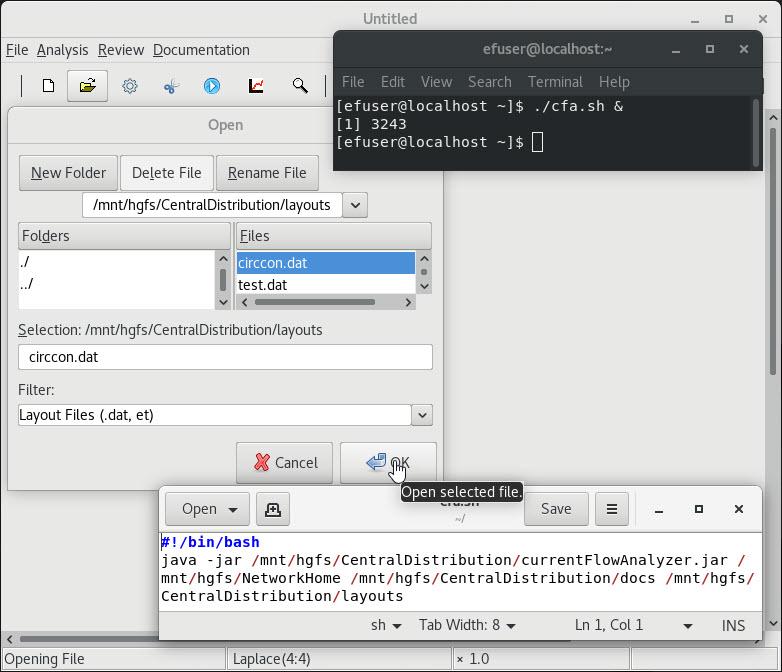
| 1 Open and solve circon.dat |
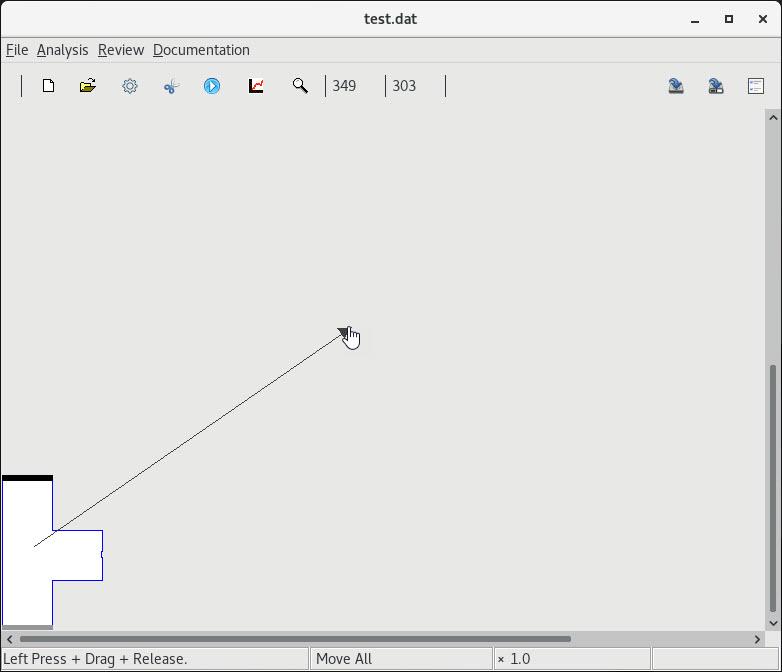
2 Open and solve test.dat |
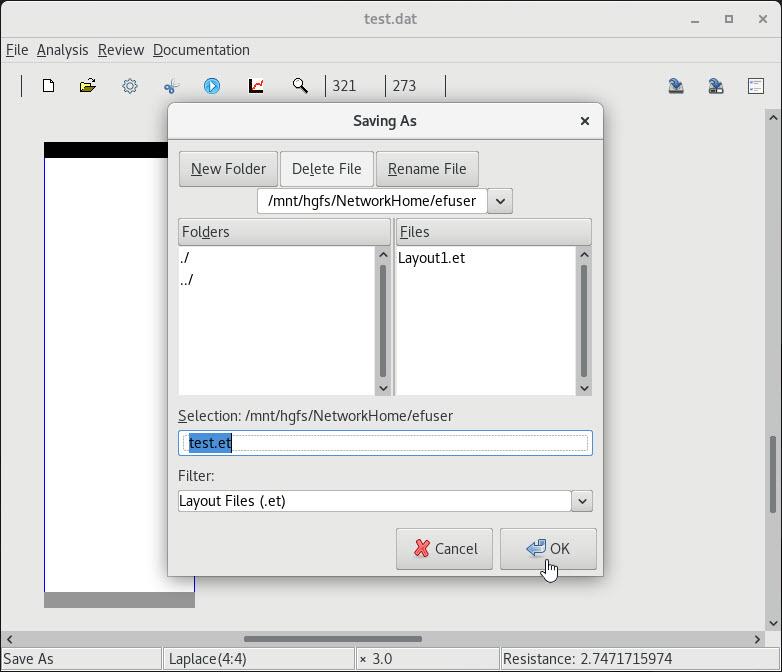
3 Save layout(resp. MRU) in ET(resp. properties)format |
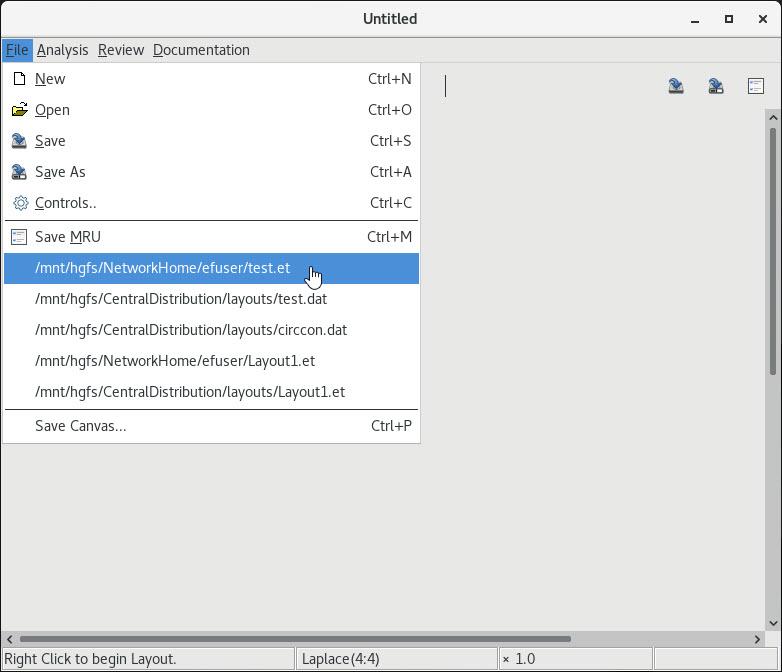
4 Restore from MRU list |
 |
 |
 |
 |
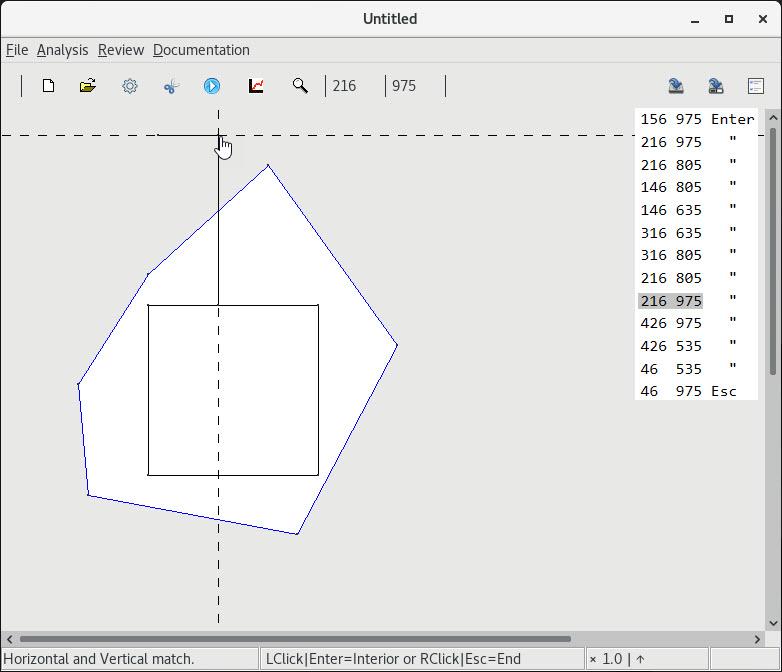
5. Base layer enclosing contact
| 1 Enclosing a base layer with a contact |
2 Trivial separation of coincident vertices |
3 Non trivial separation of coincident vertices |
 |
 |
 |
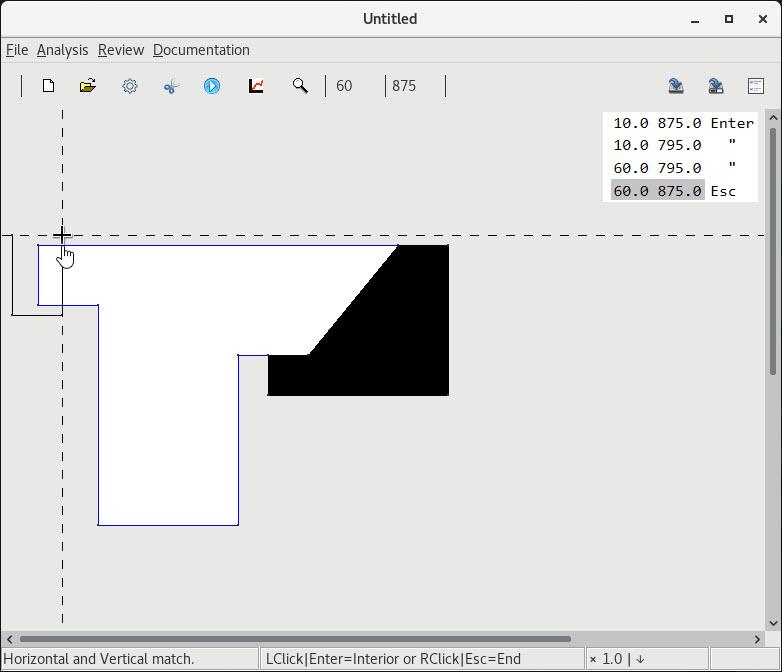
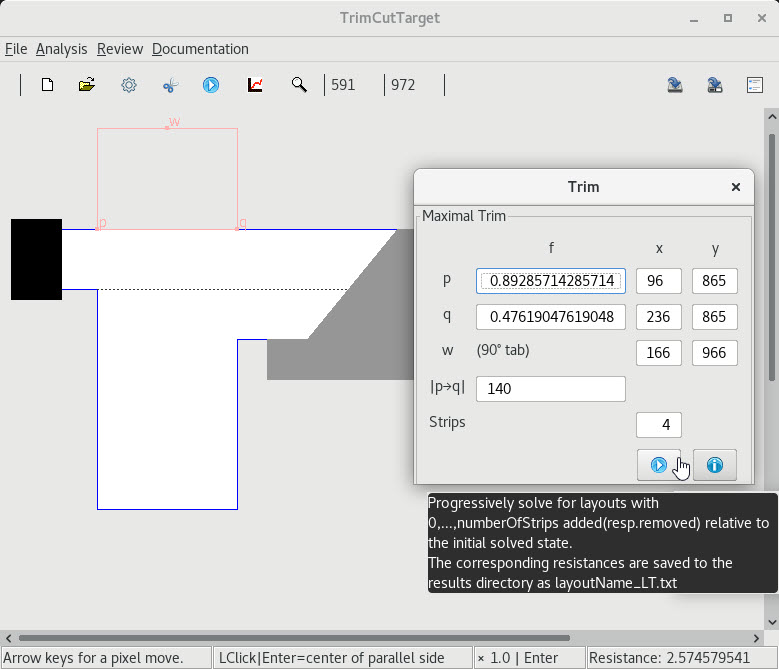
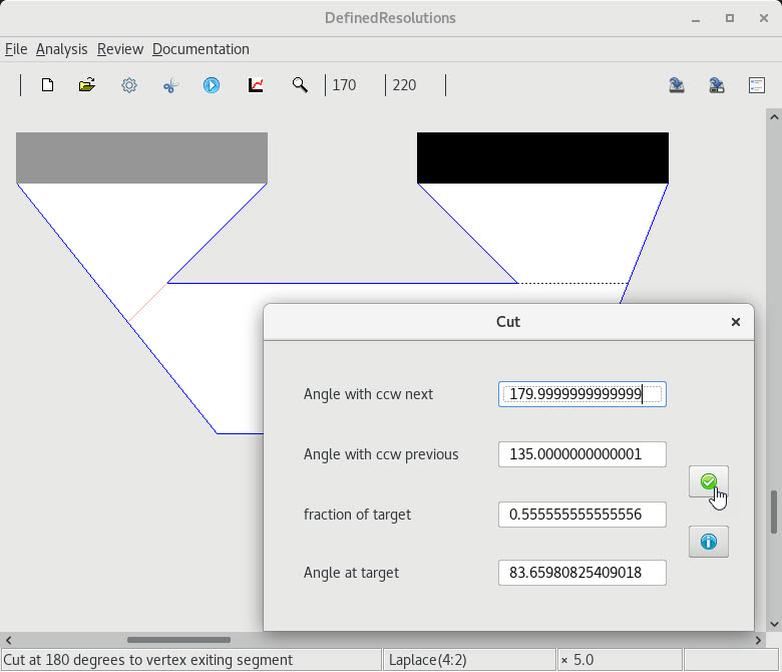
6. Trimming a base layer
| 1 A backdrop layout |
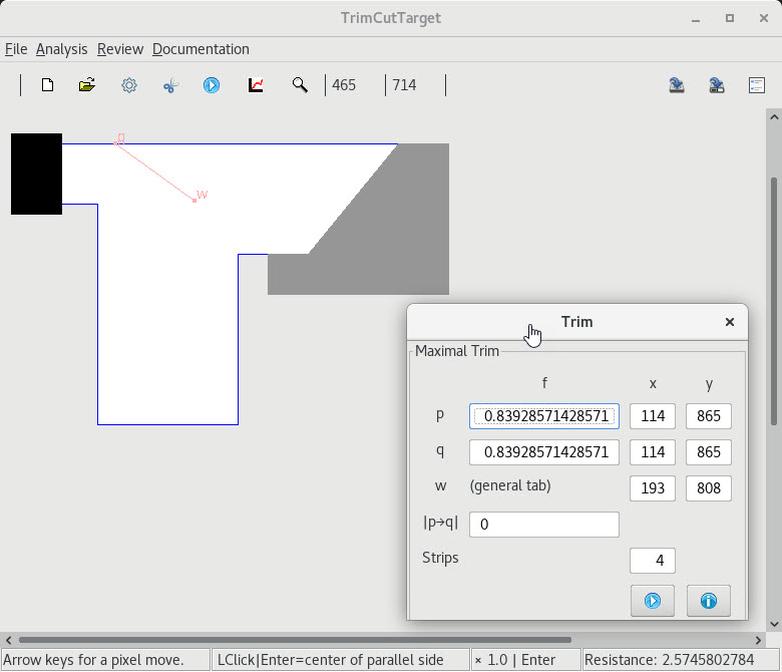
2 Adding a strip at right angles |
3 A trim curve and targeted value |
4 Adding a general strip(resp. cut) |
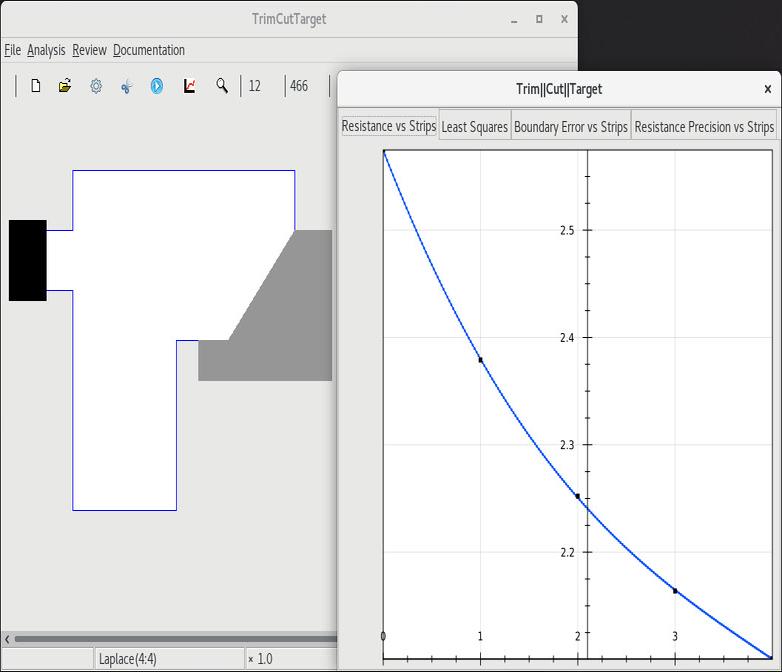
5 Removing a cut at oblique angles |
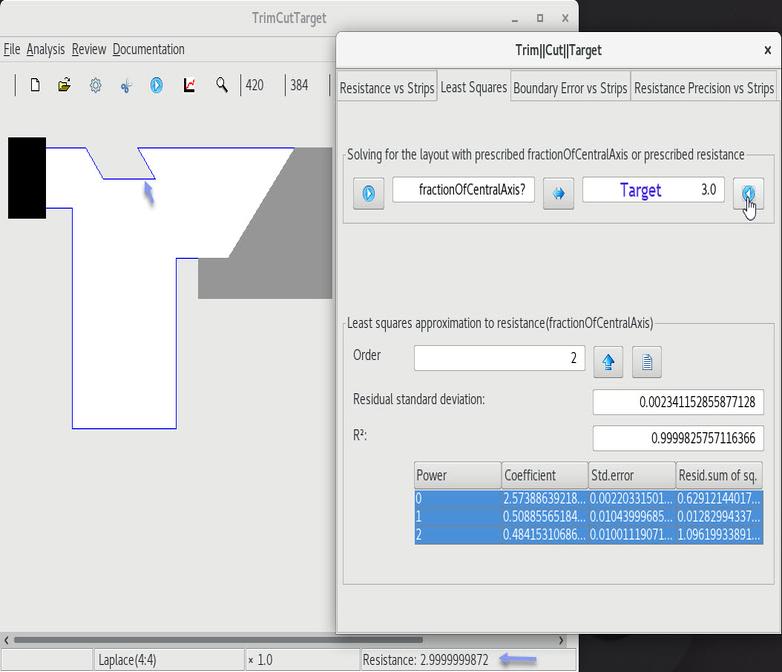
6 Targeting a cut value of 3 |
7 Targeting a cut of zero width |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
7. Trimming(resp. cutting) with user-defined continuity cuts
| 1 Trimming with default cuts |
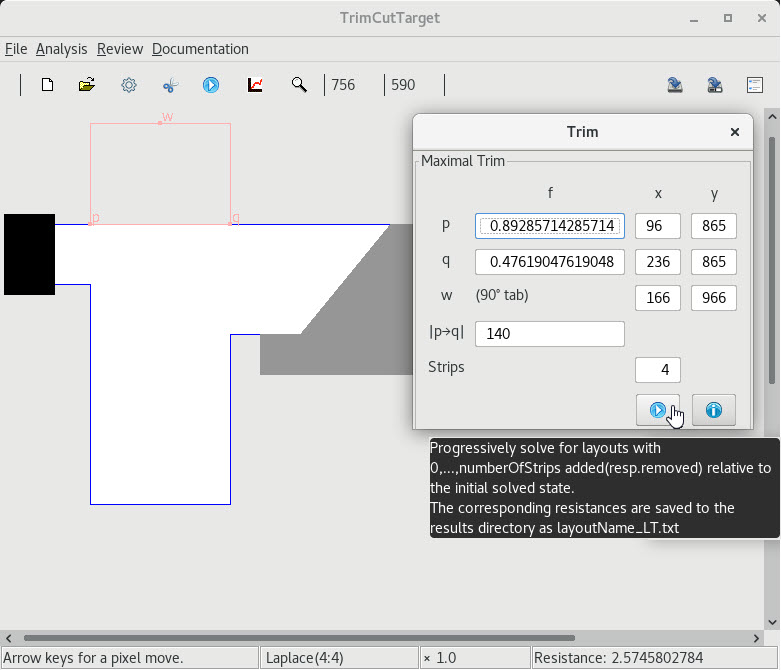
2 Prescribing cuts prior to trimming |
3 Trimming with prescribed cuts |
 |
 |
 |
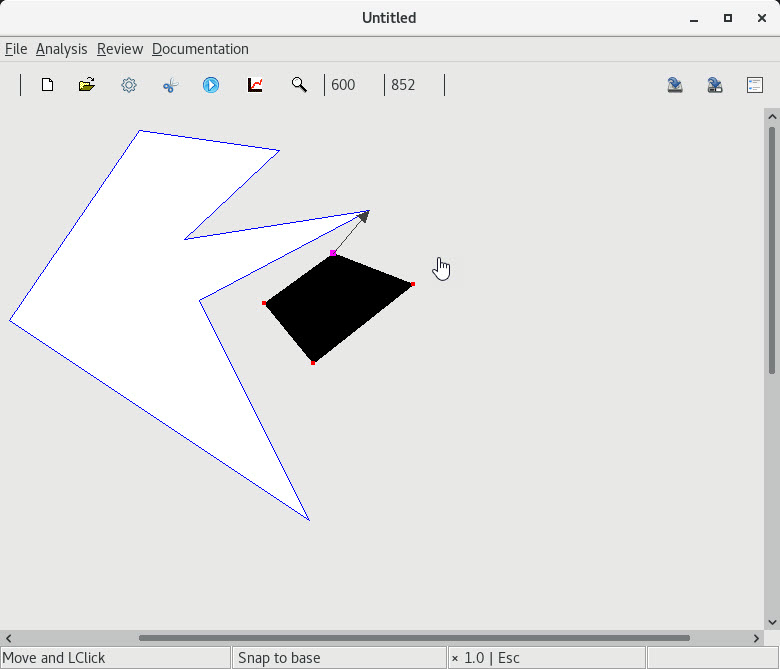
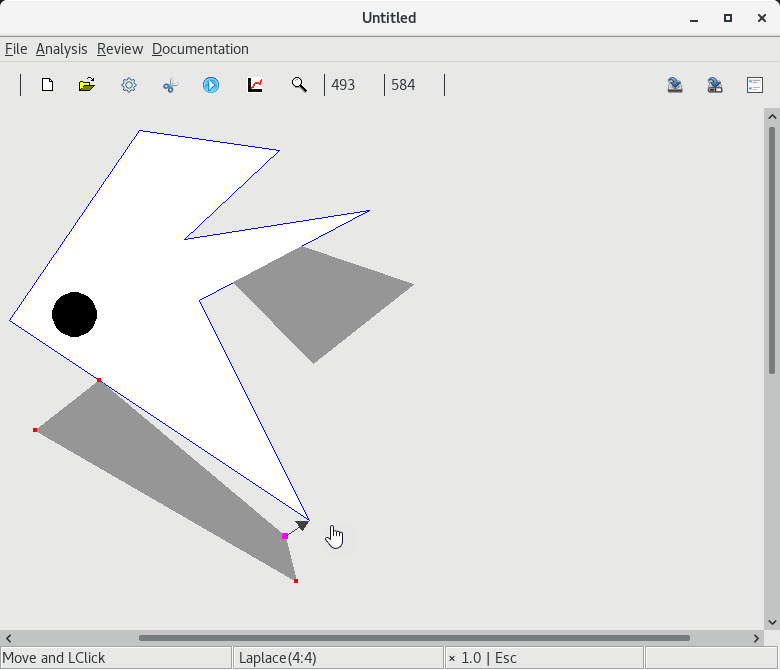
8. Attaching a contact to
| 1 an interior point of a skew segment |
2 an end of a skew segment |
 |
 |
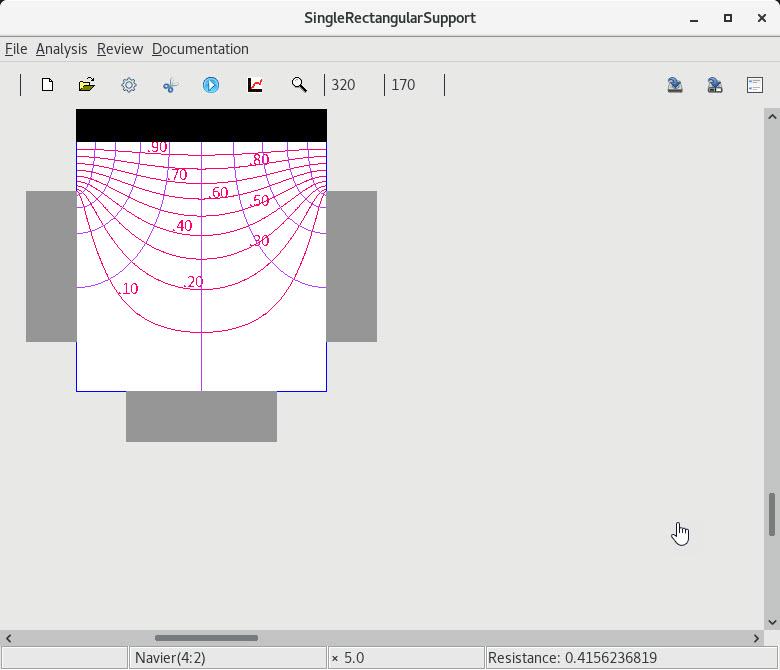
9. Range of layouts
| 1 A single rectangular subregion |
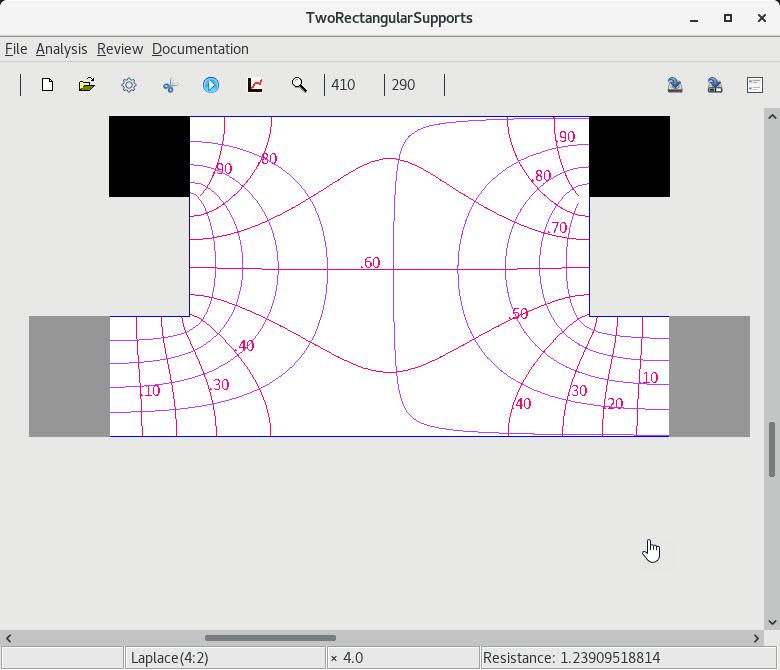
2 A pair of rectangular subregions |
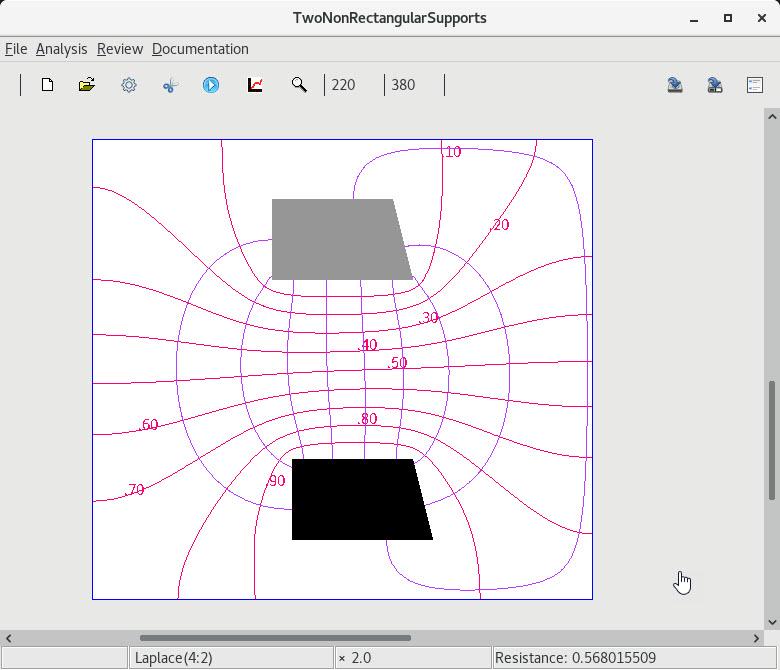
3 A pair of non rectangular subregions |
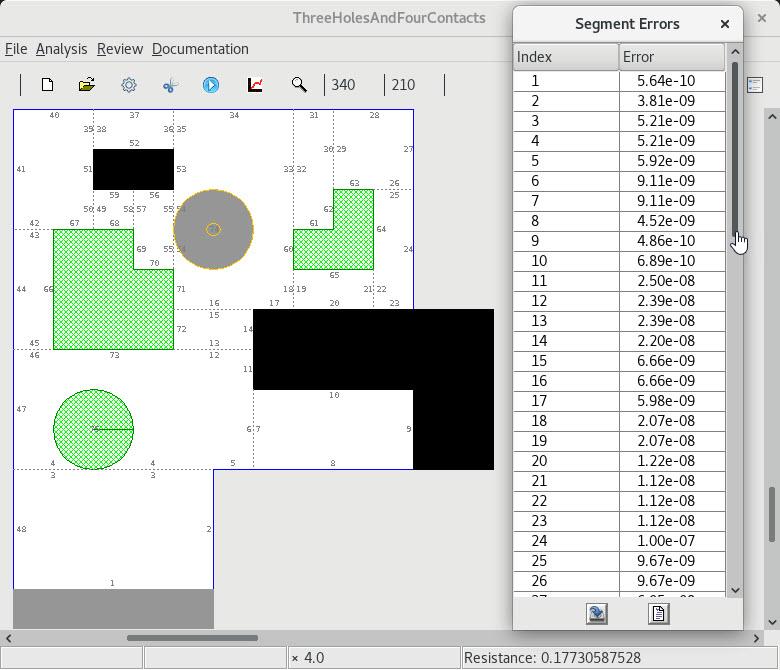
4 Layout solved by 14 rectangular subregions |
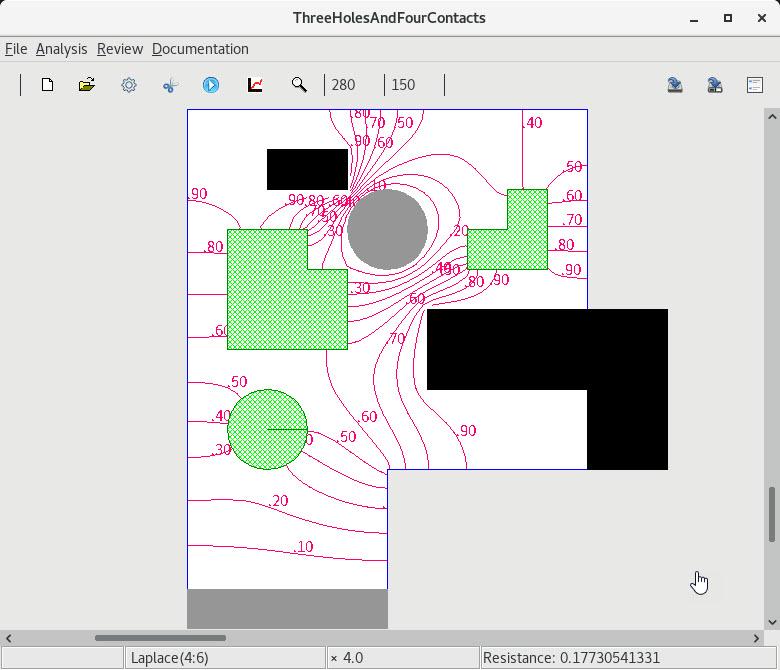
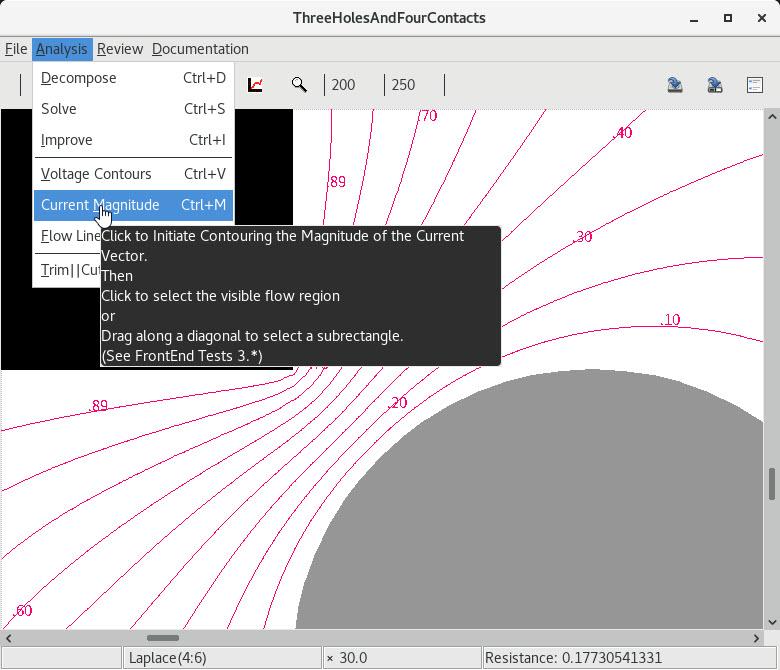
5 Contouring the entire region of flow |
6 Contouring a magnified piece |
7 Saving contour settings to the layout file |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
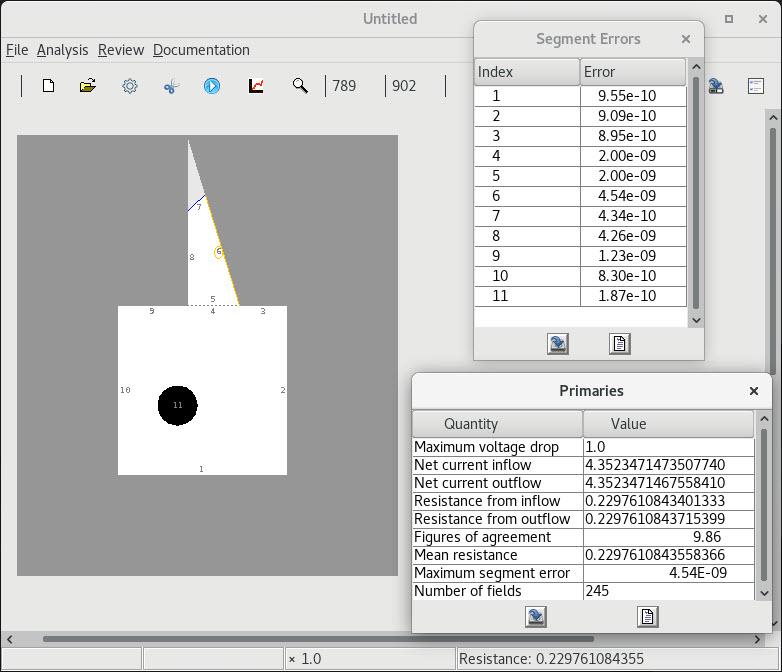
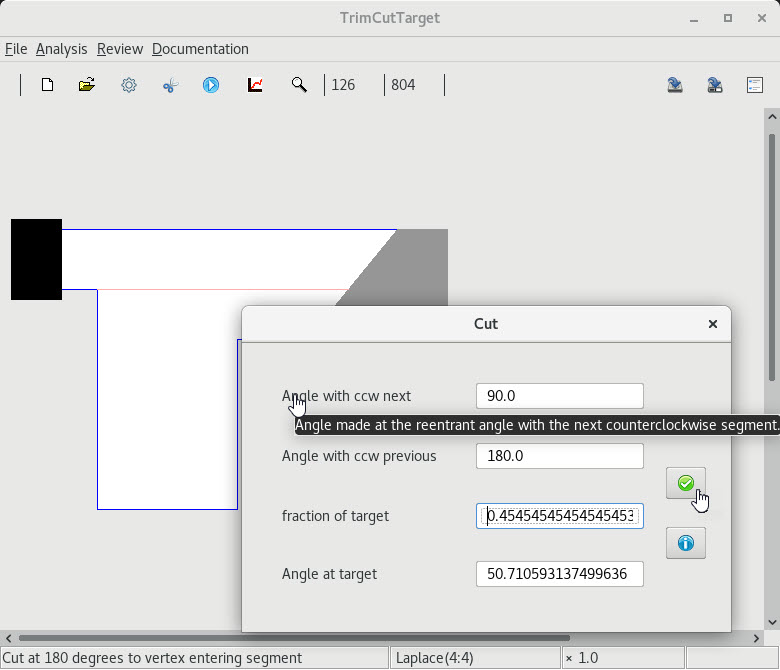
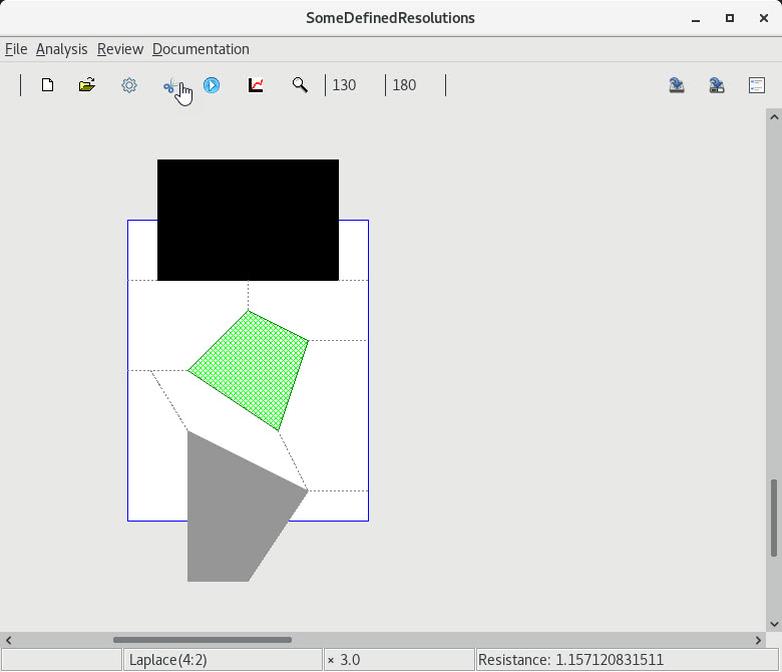
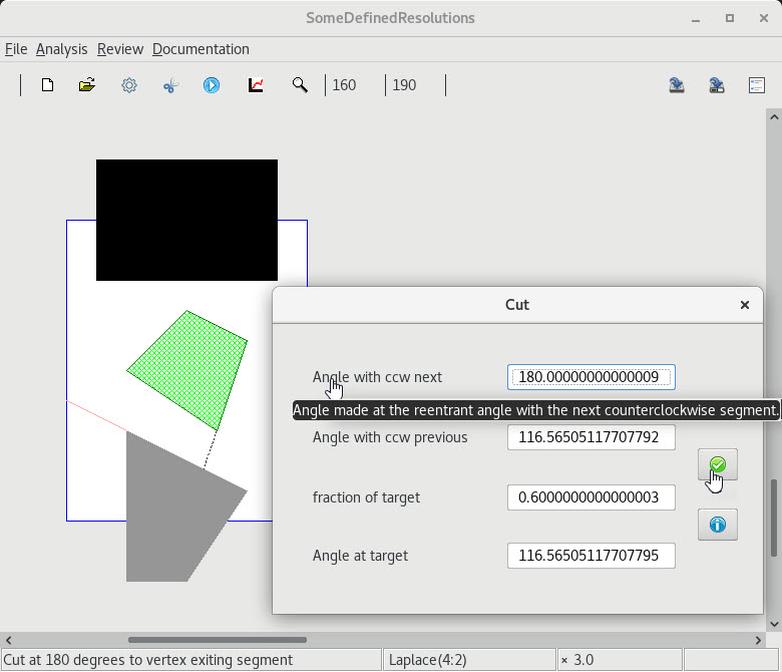
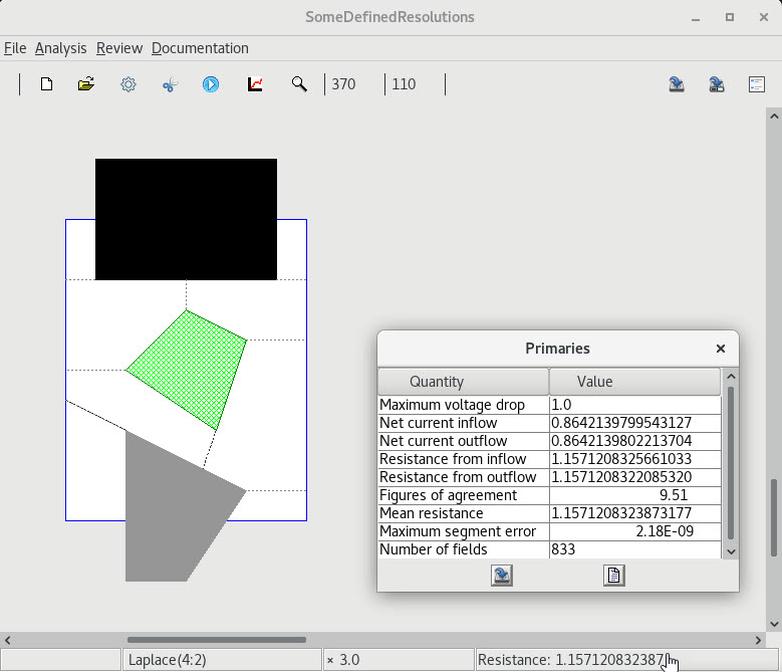
10. Resolving reentrant vertices
| 1 Default decomposition |
2 All user-defined decomposition |
3 Default decomposition |
4 Partially user-defined decomposition |
5 Automatic completion |
6 User-defined cuts are maintained in a serialization |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
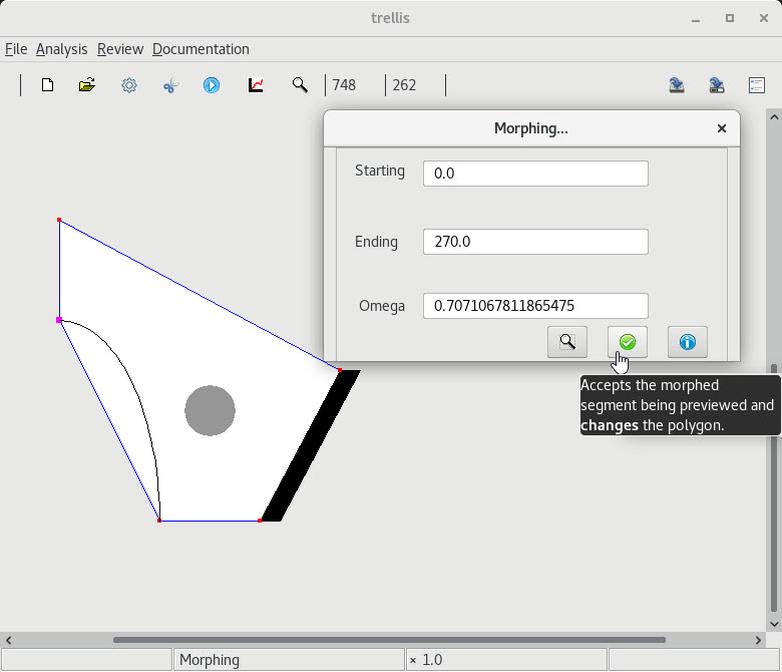
| 1 Straight segment to an elliptic arc |
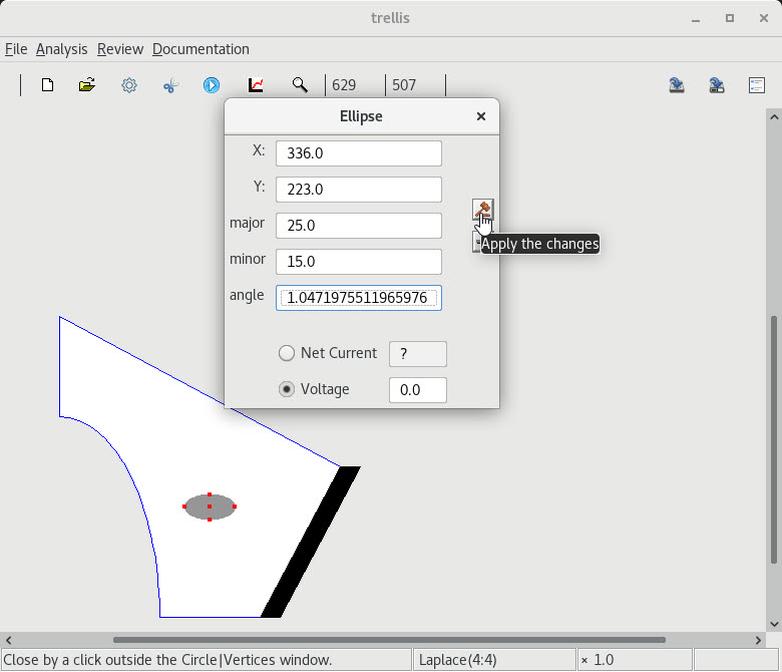
2 Change a circle into an ellipse |
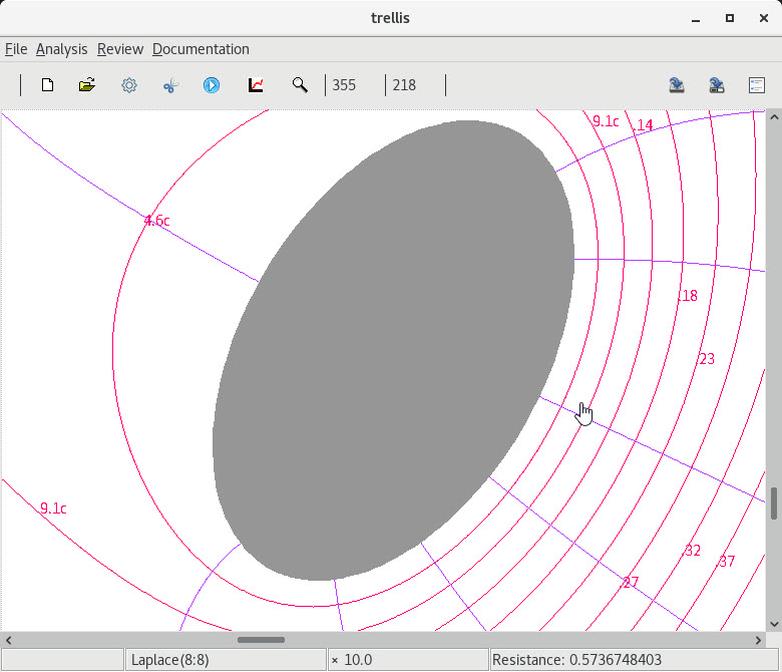
3 Solving, contouring and serializing |
4 Restarting with state restoring and solution monitoring |
5 Modifying, solving and contouring |
 |
 |
 |
 |
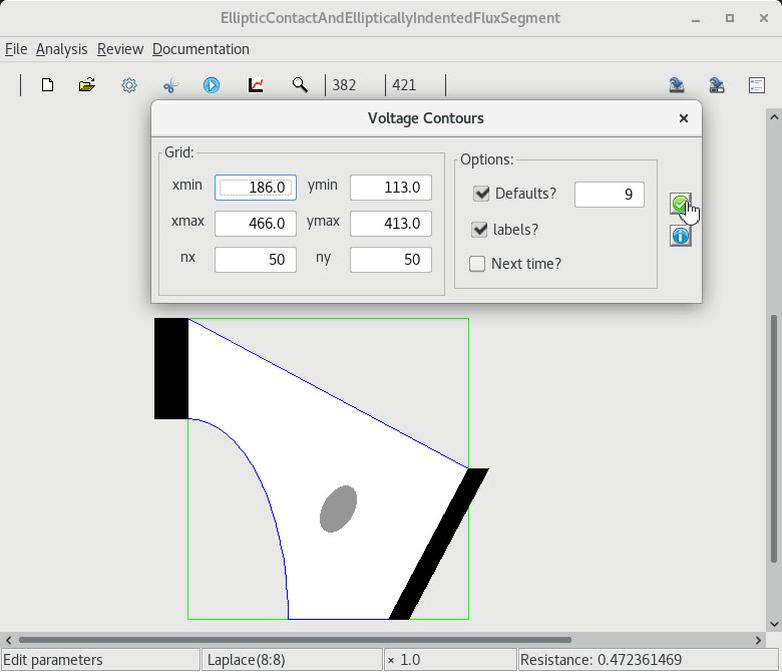 |
12. Internal line contacts and holes
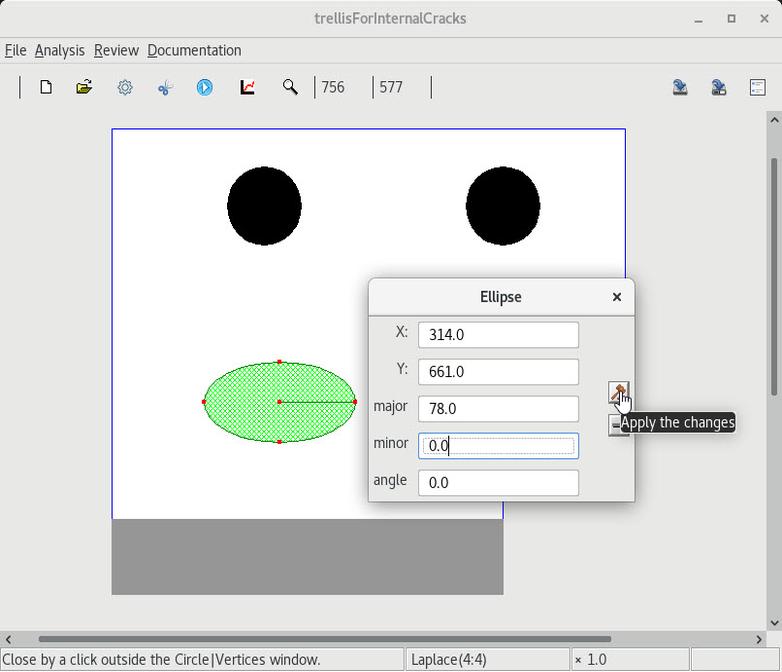
| 1 Changing a circular(resp. elliptic) hole to an ellipse(resp. crack) |
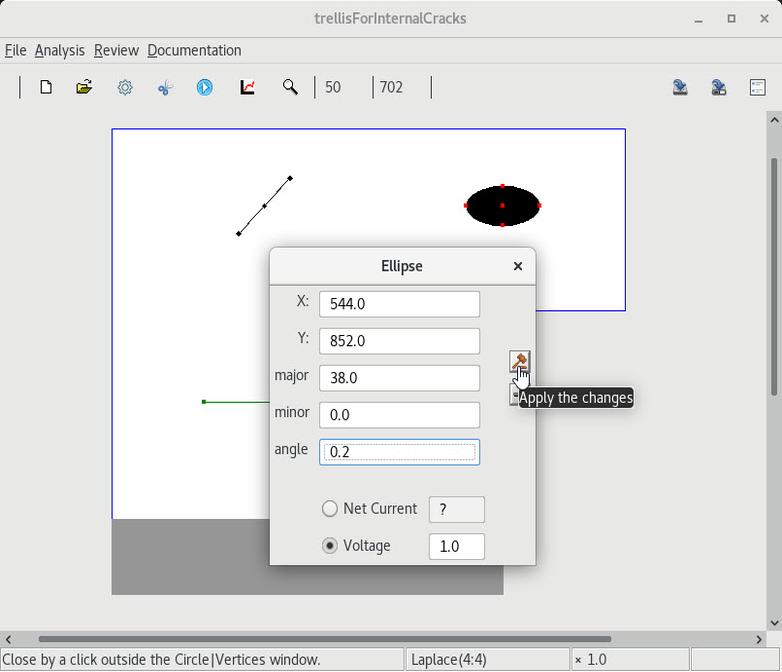
2 Changing a circular(resp. elliptic) contact to an ellipse(resp. line) |
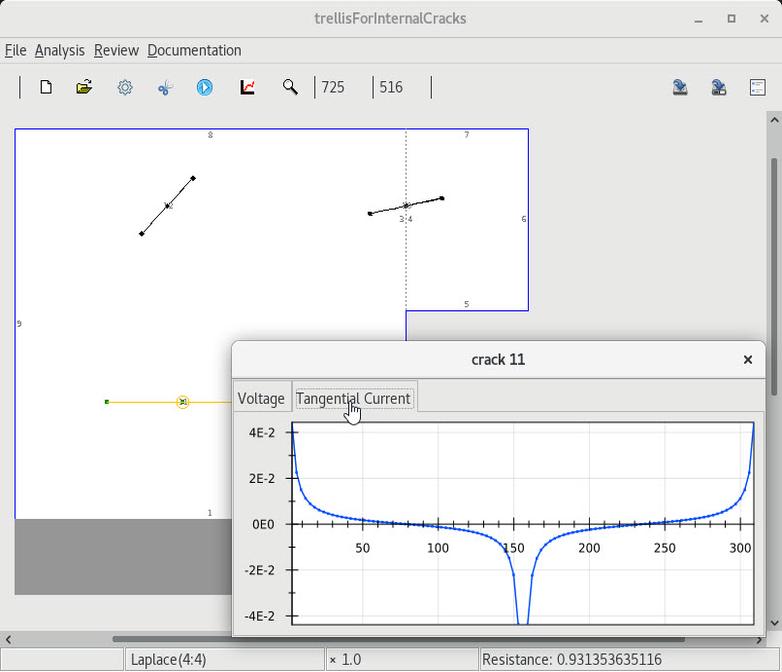
3 Responses on the crack edge edges |
4 Voltage-flowLine grid |
 |
 |
 |
 |
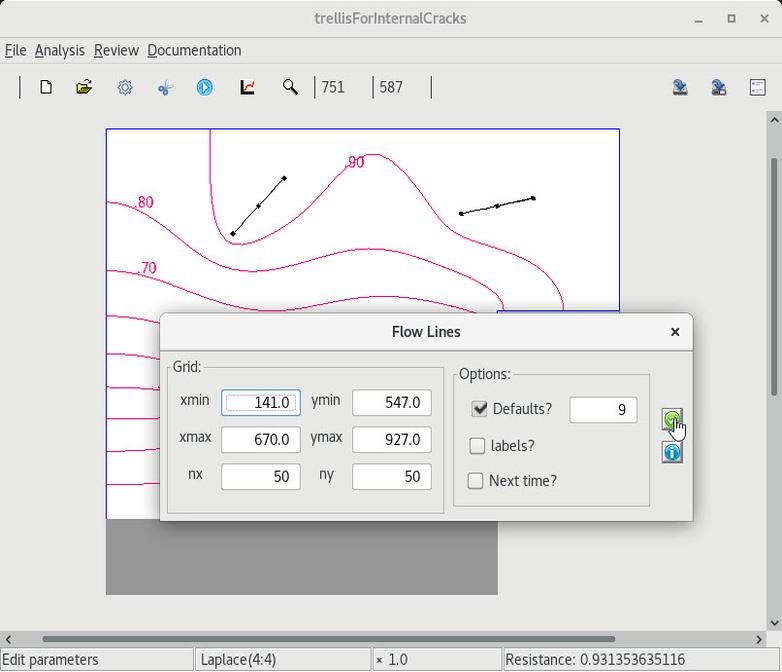 |
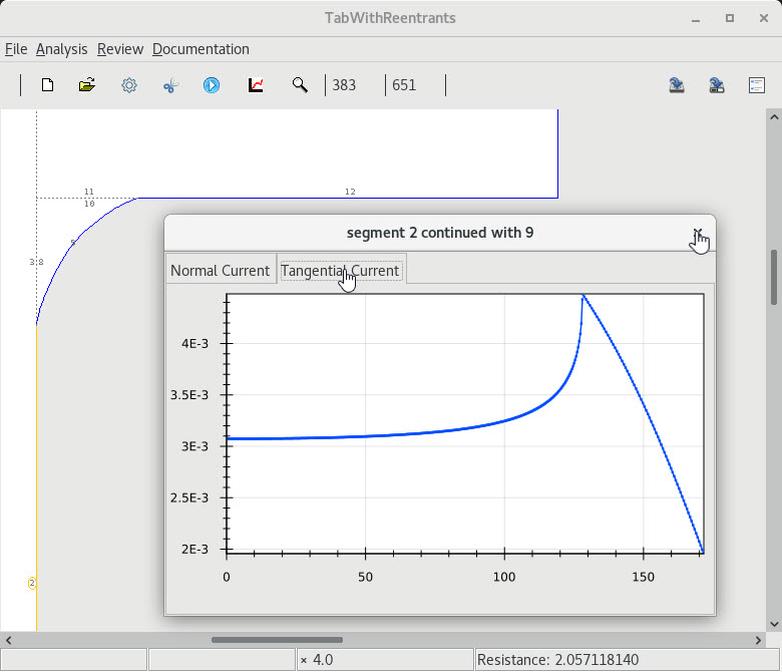
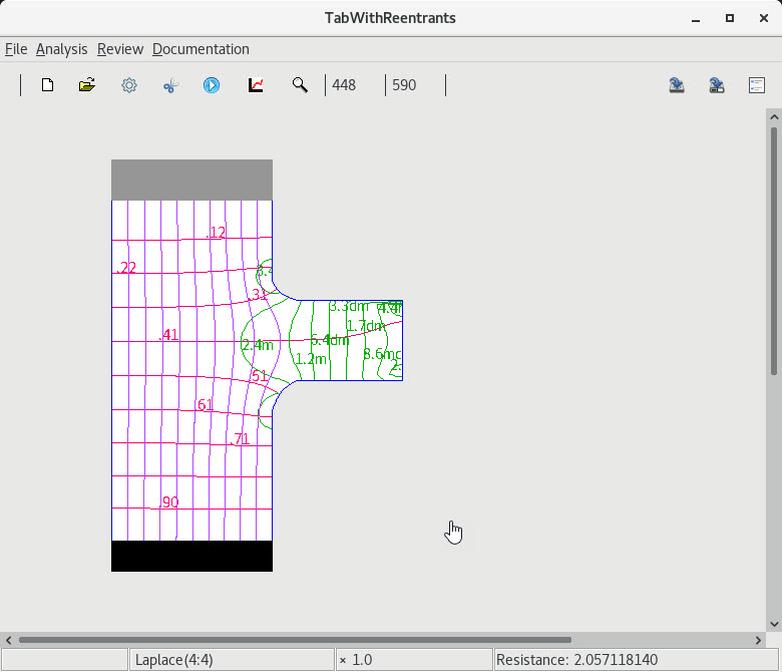
13. Rounding to remove singular base layer currents ⓘ
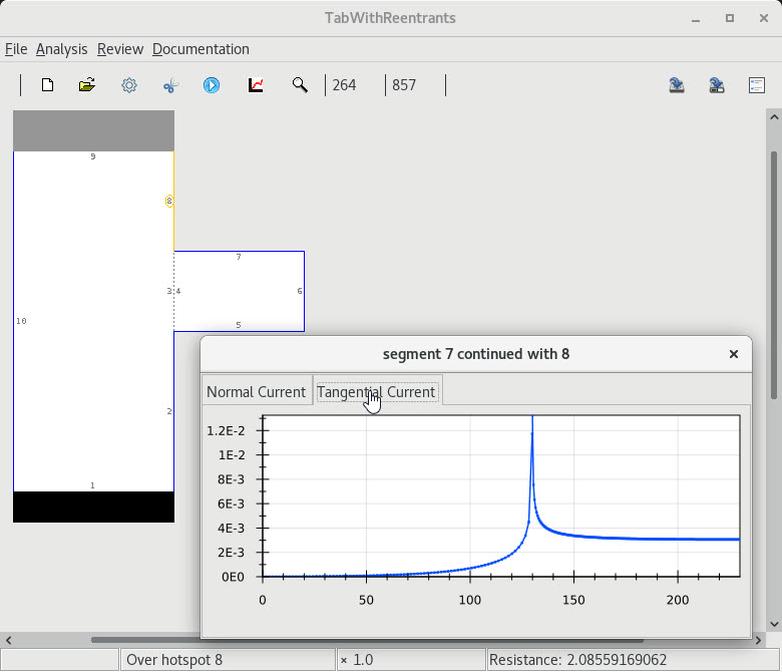
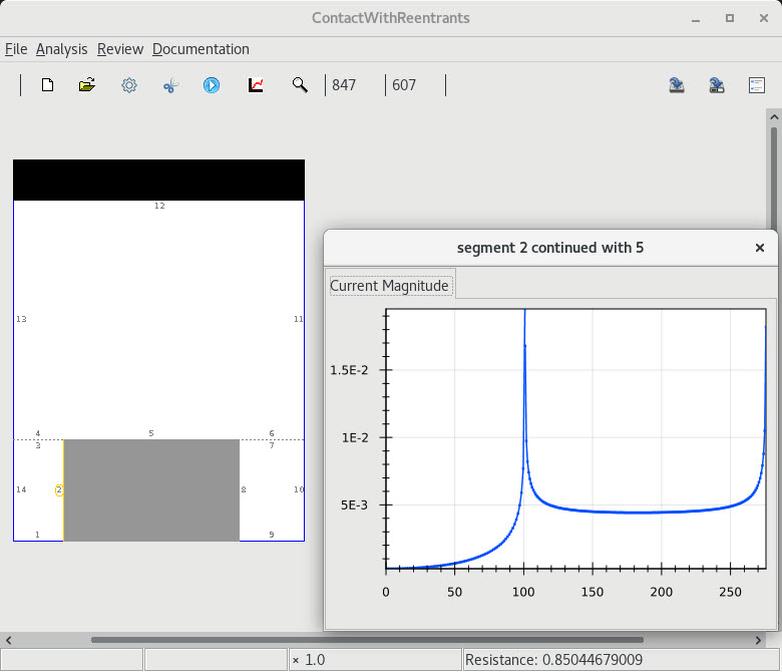
| 1 Infinite current density at a tabs reentrant corners |
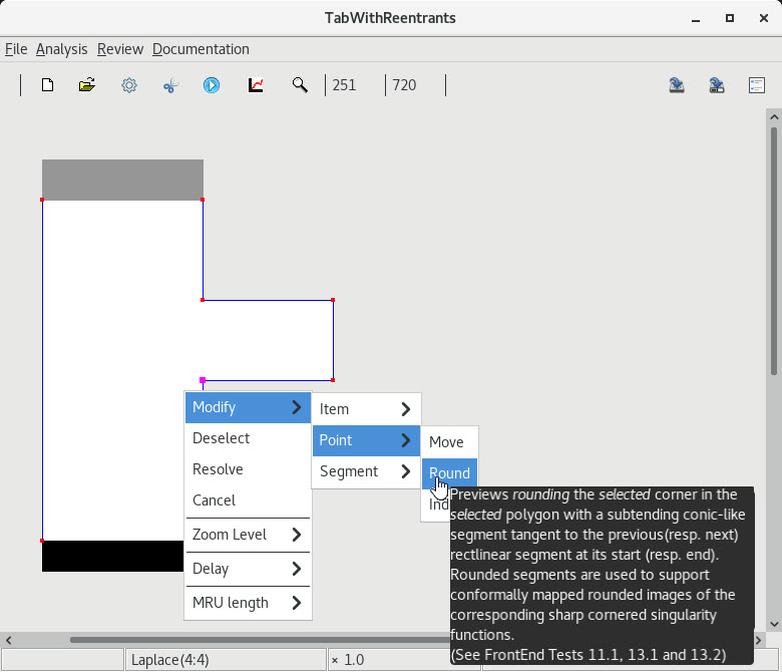
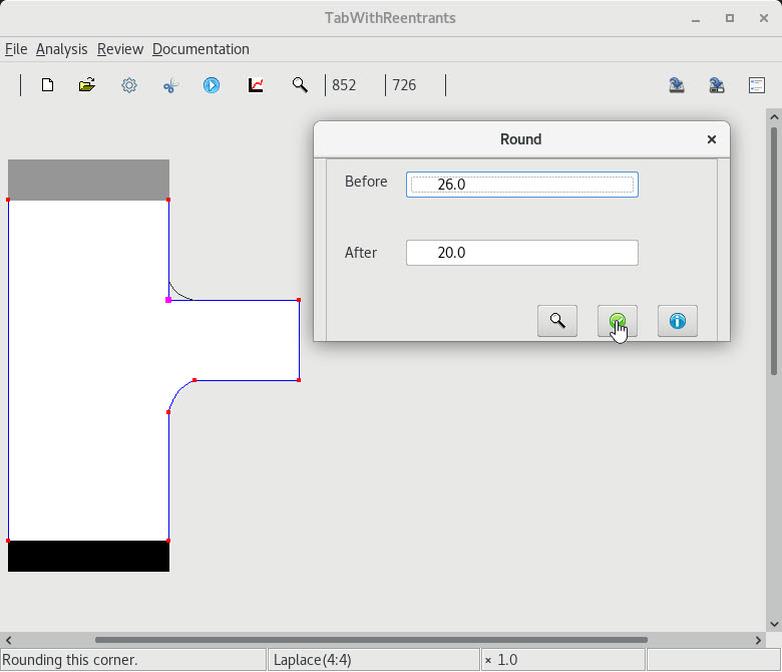
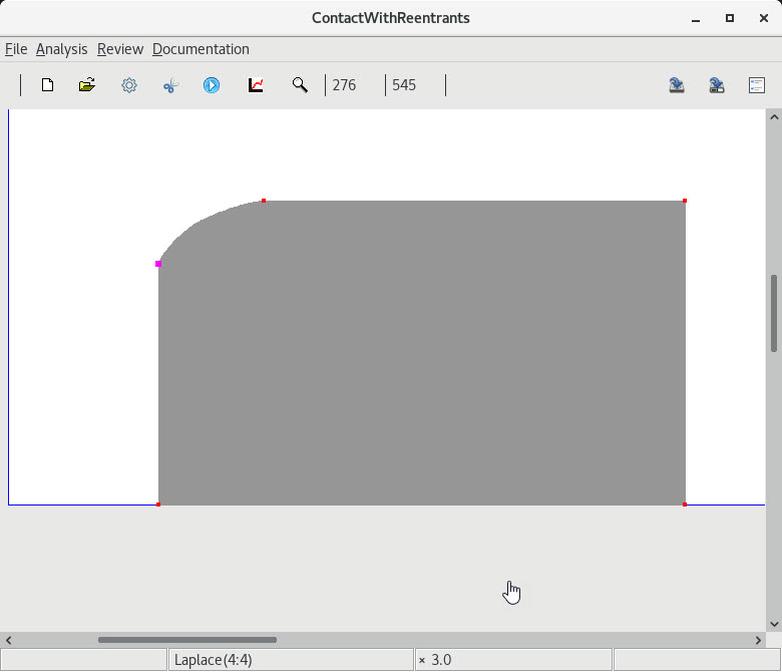
2 Select and round the lower reentrant corner |
3 Select and round the upper reentrant corner |
4 Confirm that the current density is finite |
5 Voltage-flowLine-currentDensity |
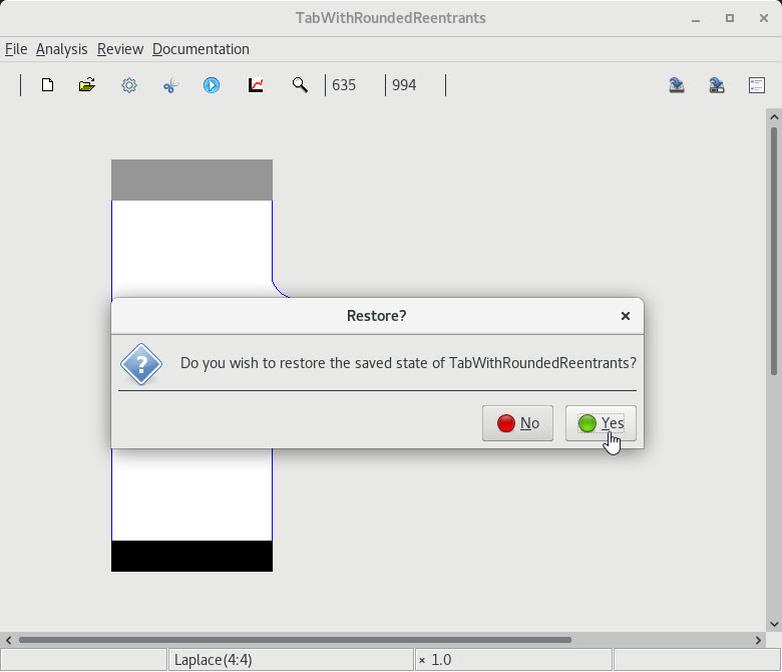
6 Restoration following a serialization |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
15. Rounding a contact with reentrant angles in the flow ⓘ
| 1 Open and solve the centrally distributed layout |
2 Singularities due to the abrupt changes in geometry |
3 Round and solve the reentrant corners of the flow region |
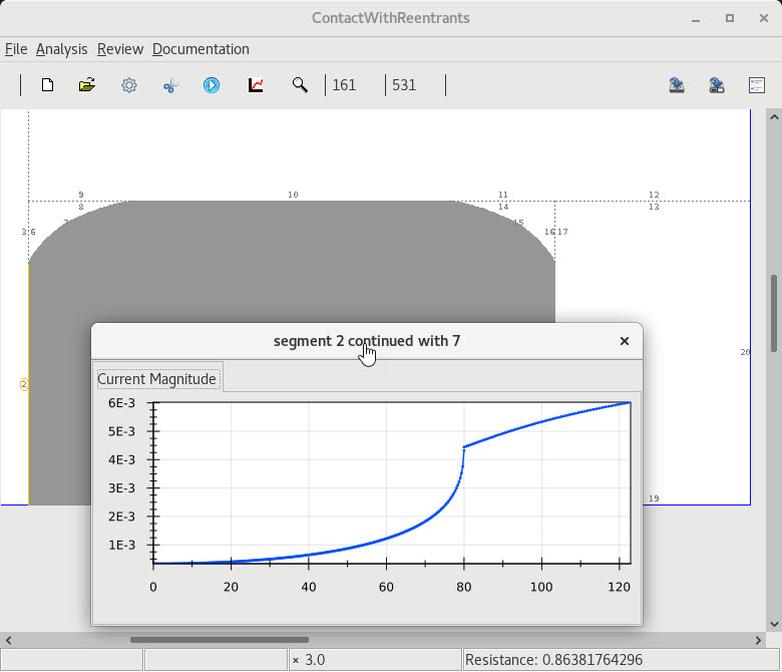
4 Non-singular current at the rounding start(resp. end) |
5 Serialize, restore and contour |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |















